Citric Acid Cycle Intermediates Are Used in Which Biosynthesis Reactions
Several of the citric acid cycle intermediates are used for the synthesis of important compounds which will have significant cataplerotic effects on the cycle. PEP is the product of the ninth reaction in glycolysis which involves the enolase-catalyzed conversion of 2-phosphoglycerate into PEP.
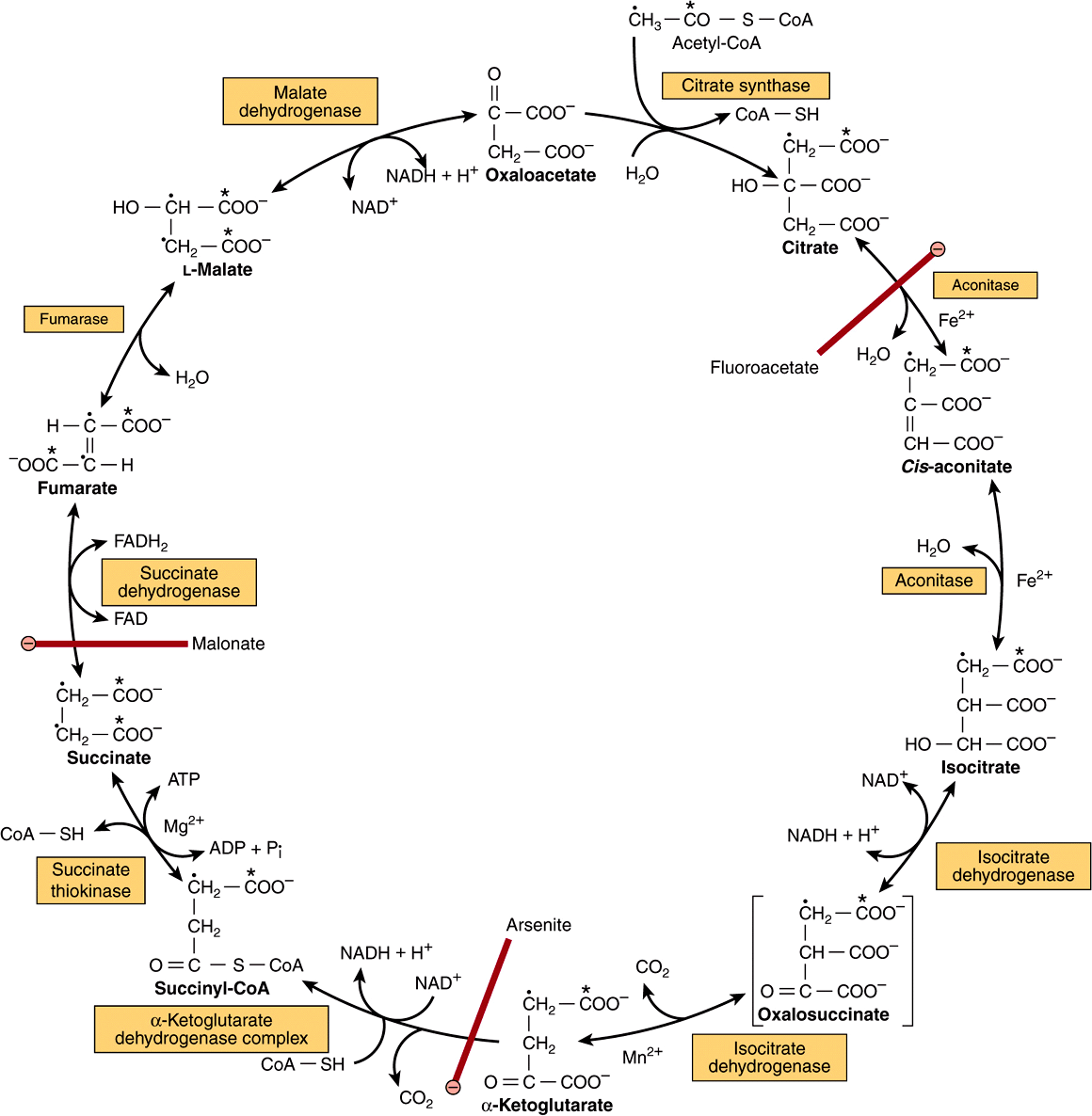
The Citric Acid Cycle The Catabolism Of Acetyl Coa Basicmedical Key
Succinyl CoA is used in the biosynthesis of heme The citric acid cycle intermediate succinyl CoA condenses with glycine in the mitochondrion to form -ALA -aminolevulinic acid in the first also the rate-limiting and the most highly regulated reaction in the heme biosynthetic pathway.

. We have already seen that malate can cross the mitochondrial membrane and give rise to oxaloacetate in. The citric acid cycle is named after citrate or citric acid. Citric Acid Cycle and Lipid Metabolism Video 1 The Citric Acid Cycle Overview The citric acid cycle takes place in the matrix or fluid of the mitochondrion.
Citric acid cycle intermediates serve as substrates for biosynthetic processes. Up to 10 cash back Correct answer. In this subheading as in the previous one the TCA intermediates are identified by italics.
Anaplerotic reactions that form intermediates for kreb cycle citric cycle. A amino acids. It is the most important metabolic pathway for the energy supply to the body.
Citric acid cycle and role of its intermediates in metabolism. The Tricarboxylic acid TCA cycle citric acid cycle is amphibolic both catabolic and anabolic The TCA Cycle Serves Two Purposes. Phosphoenolpyruvate PEP is an intermediate in glycolysis not the citric acid cycle.
In the citric acid cycle amino acid metabolism and synthesis of triglyceride in adipose tissue which is also known as lipid biosynthesis. The citric cycle is important for energy production and biosynthesis. TCA is the most important central pathway connecting almost all the individual metabolic pathways.
It is possible to derive the known intermediates of the citric acid cycle by a transition from a proposed hydrophobic catalytic site into the aqueous phase. All other molecules are indeed intermediates in the citric acid cycle. Intermediates in the citric acid cycle are used as precursors in the biosynthesis of.
The Citric Acid Cycle 7 Anabolic role of TCA cycle Intermediates of the TCA cycle serve as precursors for biosynthesis of biomolecules Many aminoacids are synthesized starting with transamination of α-ketoglutarate Porphyrins and heme are synthesized from succinyl CoA Oxaloacetate is another α-keto acid and its. Anaplerosis can be defined as the reaction that can replenish the intermediates of the pathway. Graphically represent all the regulatory mechanisms of the citric acid cycle and discuss their effect on the cycle.
In this step oxaloacetate is joined with acetyl-CoA to form citric acid. The name applied to metabolic reactions that replenish the citric acid cycle intermediates that are depleted because they were used for biosynthesis. The first reaction of the citric acid cycle is catalyzed by the enzyme citrate synthase.
A series of enzymatic reactions that occurs in all aerobic organisms. Citric acid cycle provides intermediates essential for cellular biosynthesis thus also considered to be an anabolic process. This step in fatty acid biosynthesis occurs because ATP citrate lyase is the link between the.
The citric acid cycle which is also known as the tricarboxylic acid cycle TCA cycle or the Krebs cycle is a connected series of enzyme-catalyzed chemical reactions of central importance to all aerobic organisms ie. Once the two molecules are joined a water molecule attacks the acetyl leading to the release of coenzyme A from the complex. In normal function of this cycle for respiration concentrations of TCA intermediates remain constant.
A amino acids B nucleotides C fatty acids D sterols E all of the above. Oxidize Acetyl-CoA to CO 2 to produce energy - ATP GTP - Reducing power of NADH and FADH 2 - The cycle is involved in the aerobic catabolism of carbohydrates lipids and amino acids 2. However many biosynthetic reactions also use these molecules as a substrate.
As a key regulator and precursor for fatty acid biosynthesis acetyl-CoA facilitates de novo fatty acid biosynthesis and consequently accumulation of lipids. The anabolic reactions that produce amino acids have as a starting point the intermediates of the citric acid cycle that can cross the mitochondrial membrane into the cytosol. It involves the oxidative metabolism of acetyl units and serves as the main source of cellular energy.
For example 2-oxoglutarate and oxaloacetate for amino acid biosynthesis and succinyl-coenzyme. The citric acid cycle involves eight chemical reactions that use acetyl CoA and oxaloacetate to produce carbon. The citric acid cycle intermediate succinyl-CoA can be used to synthesize porphyrins.
The citric acid cycle is the final common oxidative pathway for carbohydrates fats and amino acids. Using your own diagram illustrate the reactions that take place within thepyruvate dehydrogenase complex including all enzymes and coenzymes anddiscuss the role of the enzymes involved. ATP citrate lyase is an enzyme that represents an important step in fatty acid biosynthesis.
Anaplerosis is the act of replenishing TCA cycle intermediates that have been extracted for biosynthesis in what are called anaplerotic reactions. Citric acid cycle is also known as Krebs cycle is a cycle used by aerobic organisms to release the stored energy with the help of oxidation of acetyl CoA. They form intermediates for metabolic pathways like citric cycle.
A variety of biochemical concepts in use energy-rich-bonds group transfer substrate-channelling transporters etc can be understood to be derived from methodology commonly in use. Organisms that use oxygen for cellular respiration. Succinyl-CoA is a central intermediate of heme groups.
This is where mitochondrial DNA is found and where fatty acid breakdown takes place. It has long been appreciated that this pathway often serves a dual role in energy conservation and in the biosynthesis of key cellular intermediates for anabolic reactions. The molecule that initiates the citric acid cycle by reacting with oxaloacetate.
Replenish the citric acid cycle if it becomes depleted of intermediates by biosynthetic demands. The citric acid cycle CAC is arguably the most important central metabolic pathway in living cells. Impaired function of enzyme leads to inefficient biochemical reactions that in turn cause the observed accumulation of citric acid cycle intermediates and most importantly acetyl-CoA.

The Citric Acid Krebs Cycle Then And Now A The Citric Acid Download Scientific Diagram

The Krebs Citric Acid Cycle And Its Place In Central Metabolism In L Download Scientific Diagram

Krebs Cycle An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
The Citric Acid Krebs Cycle Boundless Microbiology

The Citric Acid Cycle Article Khan Academy

6 2 Citric Acid Cycle Related Pathways Biology Libretexts

Citric Acid Cycle Orbit Biotech
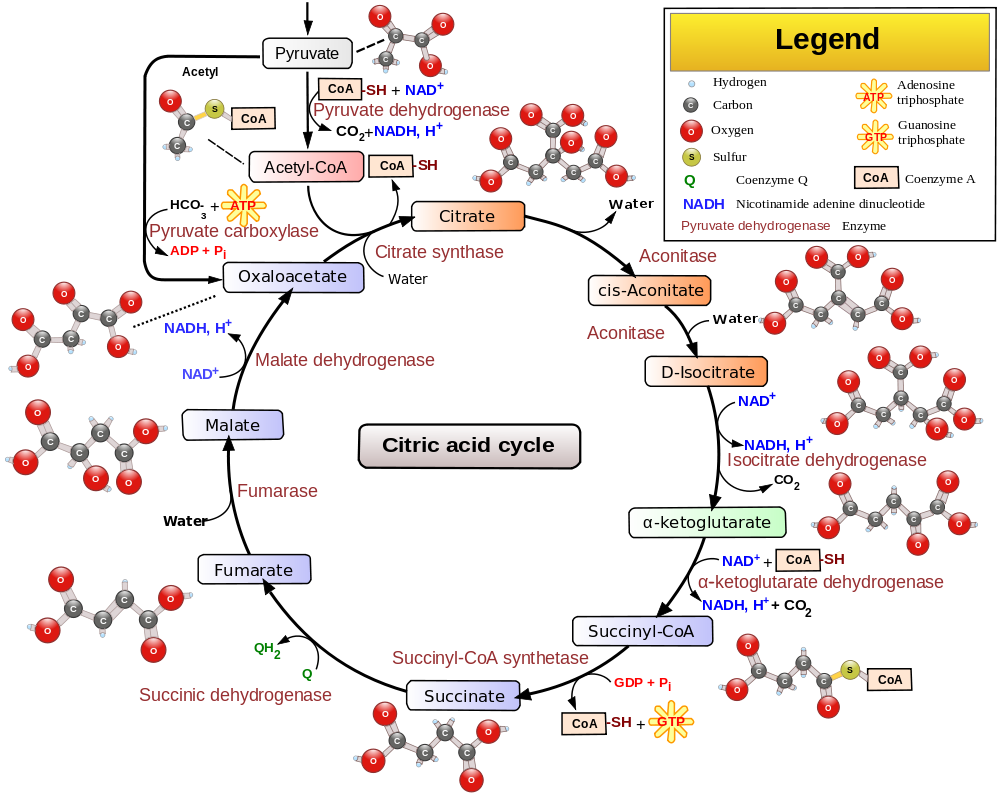
Biochemistry 08 The Citric Acid Cycle And The Electron Transport Chain
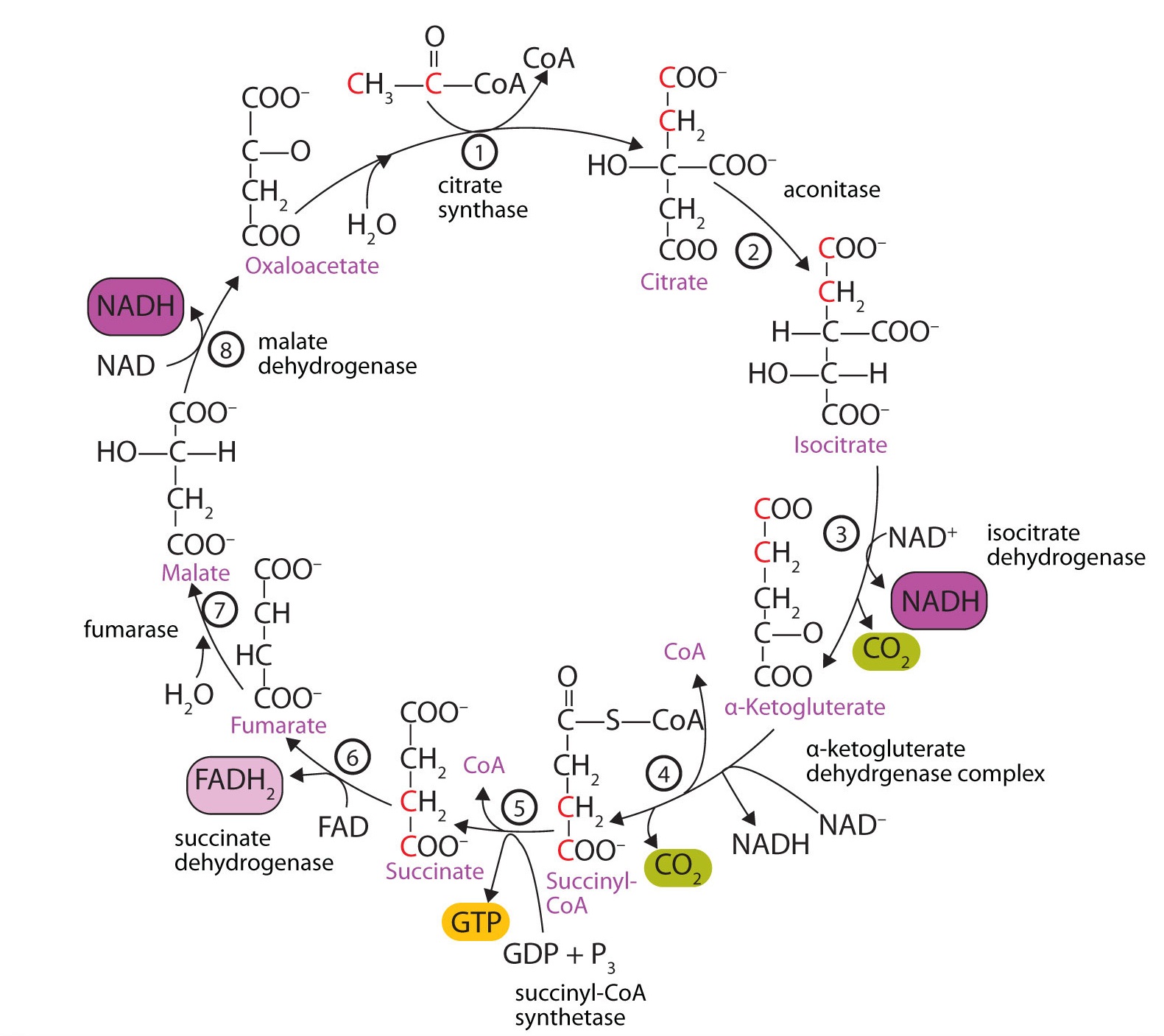
12 4 The Citric Acid Cycle And Electron Transport Chemistry Libretexts

Citric Acid Cycle Pathwayrat Genome Database

6 2 Citric Acid Cycle Related Pathways Biology Libretexts

Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle Biochemistry Britannica

Citric Acid Cycle An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

The Citric Acid Krebs Cycle Diagram Quizlet

Learn About Citric Acid Cycle Chegg Com

Krebs Cycle Activators Inhibitors And Their Roles In The Modulation Of Carcinogenesis Springerlink


Comments
Post a Comment